NBC News: Silk masks are good for skin, staying safe
UC biologist talks to NBC News about why silk is a good alternative to prevent COVID-19
NBC News talked to University of Cincinnati biologist Patrick Guerra about why silk is a good alternative fabric for face masks to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
Guerra, an assistant professor of biology in UC's College of Arts and Sciences, conducted experiments last year on different fabrics that are often used in face masks when N95 respirators are not available. UC researchers found that silk creates the most effective barrier compared to other fabrics like cotton or polyester because it repels moisture.

UC biologist Patrick Guerra studies insects such as silkworms and monarch butterflies in his biology lab. Photo/Lisa Ventre/UC Creative + Brand
“It’s still the wild west when it comes to making face coverings,” Guerra told NBC news. “But we’re finding ways to use basic science and apply what we know to improve them.”
Silk masks are becoming increasingly popular because of their comfort and fit.
“Cotton traps moisture like a sponge. But silk is breathable. It’s thinner than cotton and dries really fast,” Guerra said.
Read more about UC biologist Patrick Guerra's silk research.
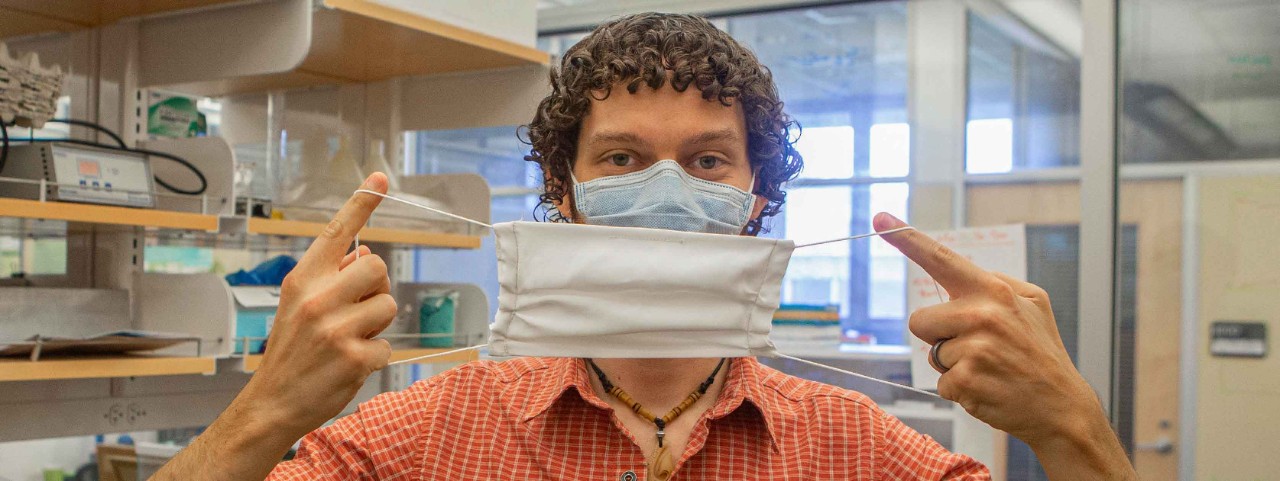
Featured image at top: UC postdoctoral researcher Adam Parlin holds up a silk face mask. A UC study found that silk masks might work better at repelling COVID-19 than cotton or synthetic masks. Photo/Joseph Fuqua II/UC Creative + Brand
Related Stories
Sugar overload killing hearts
November 10, 2025
Two in five people will be told they have diabetes during their lifetime. And people who have diabetes are twice as likely to develop heart disease. One of the deadliest dangers? Diabetic cardiomyopathy. But groundbreaking University of Cincinnati research hopes to stop and even reverse the damage before it’s too late.
Is going nuclear the solution to Ohio’s energy costs?
November 10, 2025
The Ohio Capital Journal recently reported that as energy prices continue to climb, economists are weighing the benefits of going nuclear to curb costs. The publication dove into a Scioto Analysis survey of 18 economists to weigh the pros and cons of nuclear energy. One economist featured was Iryna Topolyan, PhD, professor of economics at the Carl H. Lindner College of Business.
App turns smartwatch into detector of structural heart disease
November 10, 2025
An app that uses an AI model to read a single-lead ECG from a smartwatch can detect structural heart disease, researchers reported at the 2025 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association. Although the technology requires further validation, researchers said it could help improve the identification of patients with heart failure, valvular conditions and left ventricular hypertrophy before they become symptomatic, which could improve the prognosis for people with these conditions.
